There are many methods for determining protein concentration, and studies of various protein content determinations have also been reported. Each method has its advantages and limitations. Protein samples often contain chemical reagents that interfere with protein concentration determination. Therefore, finding suitable experimental methods to avoid interference is crucial for the accuracy of protein concentration determination. A large number of yellowish-green deposits were detected in the PEG_IL_6 sample based on the Lowry method. Urea had serious interference with the determination of protein concentration by the BCA method, which affected the accuracy of the results. We tested the two methods and further analyzed the methods.
1 Materials
Folin phenol reagent, Coomassie Brilliant Blue G_250 and 4,4-dicarboxylic acid-2,2-diquinoline (BCA) are all Sigma products; total protein (BSA) standard was purchased from Shanghai Institute of Biological Products; E. coli was crushed and β-mercaptoethanol was added to the sample; other reagents were of domestic analytical grade.
2 methods
Lowry operating reference. Sulfo-salicylic acid precipitation operation reference. The Bradford method is used to manipulate the reference. To facilitate the experiment, a small change of 0 to 500 gg/mL sample 100 L plus Bradford reagent 2 mL was performed. The absorbance was measured at 595 nm at room temperature for 5 min.
3 results
3.1 Comparison of Measurement Principles
The Lowry method is based on the principle that the protein interacts with basic copper sulphate to form a copper-peptide bond complex, which in combination with tryptophan and tyrosine reduces the phosphomolybdic acid and phosphotungstic acid in the phenol reagent to blue The principle of the determination of the compound; BCA method is the reduction of the protein valence copper ion to cuprous ion, which in combination with BCA in alkaline solution to generate purple-red complexes. Lowry and BCA are chemical methods. The sulfosalicylic acid precipitation method belongs to the physical method and the Bradford method belongs to the dye binding method. Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 is reddish-brown in acidic solution and changes to blue when combined with protein. The color depth is directly proportional to the protein concentration. .
3.2 Comparison of the determination results of three groups of samples containing five different types of proteins using four methods
The results are shown in Table 1. The standard product BSA is the same sample, and the three samples are different batches of protein.

3.3 Determination of PEG-IL-6 Protein Concentration by BCA and Bradford's Determination of Protein Concentration in Denaturation Solution
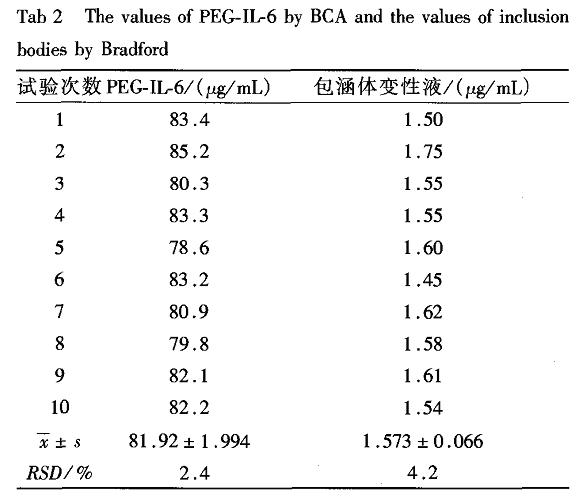
The concentration of IL-6 measured by the Lowry method was 250 μg/mL, and the concentration of the sample after PEG modification was measured by BCA method was 246 μg/mL, indicating that PEG had no effect on the BCA method. The sample with a protein concentration of 25 mg/mL in the denaturation solution of the inclusion body determined by the BCA method was measured by the Bradford method at only 1.59 mg/mL. The control experiment showed that β-mercaptoethanol in the denaturation solution of the inclusion body severely interfered with the BCA method. There is no effect on the Bradford method. Thus, the Bradford method is suitable for detecting inclusion body denaturation fluid. Table 2 shows the results of the Bradford method used to measure the same PEG-IL-6 sample by the BCA method and the same inclusion body denaturation solution sample 10 times in succession.
Table 2 Repeatability results of BCA method for the determination of protein concentration in denaturing solution of inclusion body by PEG-IL-6 and Bradford method
4 Discussion
4.1 Determination of Protein Concentration
The range of protein concentration determined by various methods is as follows: Lowry standard protein concentration range is from 10 to 100 g/mL; BCA standard protein concentration is from 20 to 1 000 g/mL; r value is still greater than 0.998; sulfo When salicylic acid precipitation standard protein concentration is set at 50 ~ 500 g / mL, r value is greater than 0.99, too high, the resulting precipitate is not easy to suspend; Bradford method is 31.25 ~ 2 000 g / mL. The linear range of the protein concentration determination method depends on the ratio of the number of moles of protein in the added sample to the number of moles of the effective chemical composition in the added reagent, rather than the ratio of the volume. Therefore, the detection range can be increased by reducing the sample volume. Cap.
4.2 Influencing factors
The main factors influencing the determination of protein by the Lowry method are certain amino acids, NH, zwitterionic buffers, nonionic surfactants, sucrose and sulfur compounds; the main factors influencing the BCA assay are sucrose, NH4+, urea, EDTA_7 J Although the sulfosalicylic acid precipitation method overcomes the above various factors, the precipitation properties formed by different proteins vary greatly. As shown in this experiment, the determination of tetanus toxoid and IL-6 protein content error using the bovine serum albumin standard can exceed 100%, and the smaller the protein concentration, the greater the error, so when using this method to determine the protein content should be selected the same Or similar protein standards. The main factors affecting the Bradford method are glycerin, acetic acid, detergents, and some alkaline buffering systems. Since the yellow precipitate was produced when the PEG-IL-6 was measured by the Lowry method and precipitated rapidly to the bottom of the tube, a uniform absorbance could not be measured with a spectrophotometer. Therefore, the Lowry method cannot be used to determine the concentration of PEGylated proteins such as PEG-IL-6, but the BCA method can be used. The denaturation and refolding fluids of inclusion bodies often contain urea and β. Mercktoethanol, these substances will interfere with the BCA assay, so the BCA method is not suitable for containing urea and beta. Determination of protein content in the denaturation liquid of mercaptoethanol. According to Table 1, the sulfosalicylic acid precipitation method has a large deviation from each sample. Therefore, the precipitation method must be determined with a reference substance that is homogenous to the sample and has a known protein content. It is also not suitable for detecting PEG-IL- 6 and denaturation fluid protein determination. The results shown in Table 2 show that the BCA assay detects PEG-IL-6 with less reproducibility (RSD < 5%), whereas the Bradford method can be unaffected by the reducing material in the denaturing solution, in the denaturing solution of the inclusion body. The detection of protein concentration is more accurate and reproducible (RSD < 5%). Therefore, it is best to use the BCA method for PEG-IL-6 and other PEG-modified protein concentrations. For inclusion body denaturing solutions, which contain reducing substances, the Bradford method is the best method for determining the protein concentration.
DUDU NEW ENERGY AUTOMOBILE COMPANY , https://www.duduelectriccar.com