With the increase in the introduction of foreign technology in petrochemical projects, the diversification of construction investment and the increase in the amount of investment, construction units, especially foreign joint venturers or collaborators, have paid increasing attention to the quality of projects, and the petrochemical water supply and drainage pipelines use API (American Petroleum Institute ) Standard manufactured valves are increasing. In this case, engineering technicians at the construction site are required to test such valves in accordance with the current API valve test project and the test proportion determined in accordance with the current relevant construction specification. The following describes the test items and test proportions of gate valves, globe valves, and butterfly valves commonly used in API standards for petrochemical water supply and drainage pipelines.
1 Common API Standards for Petrochemical Water Supply and Drainage Pipes to Produce Valves - Test Items for Gate Valves, Globe Valves, and Butterfly Valves
The current API standard for manufacturing valve tests is Valve Inspection and Testing API STANDARD 598 NINTHEDITION, SEP-TEMBER 2009. The following describes the commonly used API standards for petrochemical water supply and drainage pipelines to produce valves—gate valves, globe valves, and butterfly valves. Test items include shell tests, upper seal tests, low-pressure seal tests, and high-pressure seal tests.
1.1 Valve Test Project
The test items for gate valve, globe valve and butterfly valve are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1 Valve test items with DN ≤ 100 (NPS ≤ 4) and Class ≤ 1500 and DN> 100 (NPS> 4) and Class ≤ 600
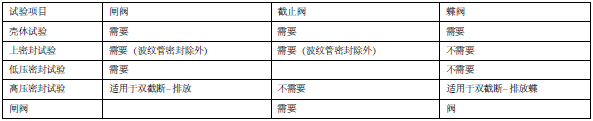
Table 2 Valve test items with DN ≤ 100 (NPS ≤ 4) and Class> 1500 and DN> 100 (NPS> 4) and Class> 600

1.2 valve test medium
(1) Shell test, high-pressure sealing test and the test medium listed in Table 2 for the upper seal test are kerosene or water. The temperature of the test medium should be within the range of 5 to 40°C.
(2) The test medium for the low-pressure sealing test and the above-mentioned upper sealing test listed in Table 1 is air or inert gas.
(3) When austenitic stainless steel valves are used for water tests, the chloride ion content in the water must not exceed 100 mg/L.
1.3 Valve test pressure
The test pressures of gate valve, globe valve and butterfly valve are shown in Table 3 and Table 4.
Table 3 Valve Housing Test Pressure

Note: The 38°C pressure rating of the valve is marked on the body or valve tag (nameplate) and in the quality certificate.
Table 4 Valve seal test, low pressure seal test, high pressure seal test pressure
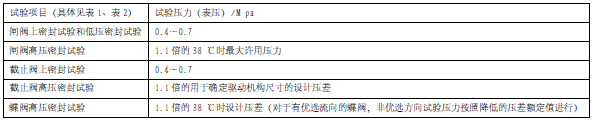
NOTE: The design pressure differential used to determine the design dimensions of the drive mechanism, the maximum permissible pressure at 38°C, and the design pressure differential at 38°C, the drop pressure differential rating for the non-preferred direction of the preferred flow direction of the butterfly valve are specified in the purchase specification.
1.4 The shortest duration of the valve test
See Table 5 for the shortest duration of the test pressure for the gate, globe, and butterfly valves.
Table 5 Minimum duration of valve test

Note: The duration of the high-pressure seal test of the double-cut-discharge gate valve and double-cut-discharge butterfly valve is not less than twice the value of this table.
1.5 Valve test allowable leakage rate
1.5.1 Gate valve, globe valve, butterfly valve test allowable leakage rate
(1) For valves with adjustable stem seals, sealing through the stem should not cause rejection of the valve during the test duration of the valve housing, but the manufacturer shall be able to demonstrate that the stem seal can maintain a minimum pressure of 38°C at the valve. Visible leakage occurred. No visible droplets or moisture are allowed in the rest of the valve housing.
(2) For valves with non-adjustable stem seals (O-rings, fixed single rings, and similar parts), the valve stem seal and the rest of the valve housing are not allowed to have visible droplets or moisture during the valve housing test duration.
1.5.2 Sealing Test Permitting Leakage Rate on Gate Valve and Globe Valve
(1) The gate valves and globe valves listed in Table 1 that use gas (air or inert gas) for the upper seal test shall not allow visible leaks to occur at the upper seals, and may be tested by applying a neutral foaming agent.
(2) The valves listed in Table 2 that use liquid (kerosene or water) for the upper seal test do not allow visible droplets or wetting on the upper seal.
1.5.3 Gate valve, globe valve, butterfly valve low pressure sealing test and high pressure sealing test allow leakage rate
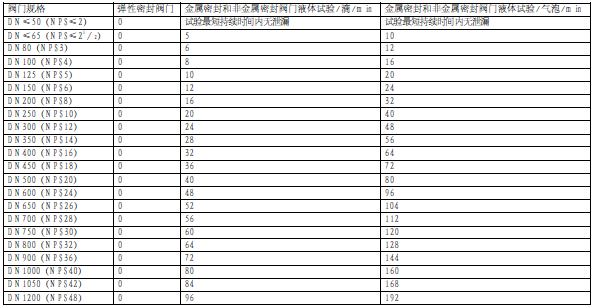
As listed in Table 1 and Table 2, gate valves need to be tested for low-pressure sealing and high-pressure sealing. The closing valves and butterfly valves need only be subjected to high-pressure sealing tests. For valve low-pressure and high-pressure seal tests, no visually permissible leakage through the disc, back of the seat ring, shaft seal (if any) and no mechanical damage are permitted - elastic seats and seals Plasticity or permanent deformation is not considered as a mechanism of damage. For the duration of the test, the allowable leakage rate of the test medium (air or inert gas for the low-pressure seal test and kerosene or water for the high-pressure seal test) is shown in Table 6.
Table 6 Valve Low Pressure Seal Test, High Pressure Seal Test Allowable Leakage Rate
1.6 Valve test requires special instructions
1.6.1 The best sequence of test for gate valve, globe valve and butterfly valve
The best sequence for gate valve, globe valve and butterfly valve test is: shell test → high pressure seal test → upper seal test and low pressure seal test. If the valve test is not performed in this order, it will lead to the determination of the extension of the unqualified valve time.
1.6.2 Operating Torque to Close the Valve During Low Pressure Seal Test and High Pressure Seal Test
When performing the low pressure seal test and the high pressure seal test, the operating torque for closing the valve shall not exceed the published value of the valve manufacturer.
1.6.3 High Pressure Seal Test and Low Pressure Seal Test of Gate Valve
The high pressure seal test and low pressure seal test of the gate valve (except the double cut-discharge gate valve) should be followed by pressurizing each end of the closed valve and open to the atmosphere at the other end to check for leaks at the open end seal faces. For double cut-discharge gate valves, the high pressure seal test and low pressure seal test pressurize each end of the closed valve in turn through the valve port. Leakage into the body cavity of the valve can be checked through the exhaust port (or vent in other locations) at the bottom of the valve. .
1.6.4 High Pressure Seal Test of Globe Valve
The high-pressure sealing test of the shut-off valve was pressed against the flap from under the flap.
1.6.5 Butterfly Valve High Pressure Seal Test
(1) For seals or flexible liners designed to use Class 125 or Class 150 flanged butterfly valves (API609 Class A valves), high pressure seal testing is only required in one direction. For other flexible sealing butterfly valves (API609B type valves), a bidirectional high pressure sealing test is required.
(2) For a butterfly valve with a preferred flow direction, the preferred direction is to conduct a high pressure seal test at a design pressure difference of 1,8 times the 38°C, and the non-preferred direction test pressure is to be subjected to a high pressure seal test at a reduced pressure differential rating.
2 Commonly used API standards for petrochemical water supply and drainage pipelines to manufacture valves - test proportions of gate valves, globe valves and butterfly valves
2.1 Commonly used API standards for petrochemical non-metallic water supply and drainage pipelines - Valves, globe valves, and butterfly valves
For petrochemical non-metal water supply and drainage pipelines commonly used API standard manufacturing valves - gate valve, cut-off valve, butterfly valve, the valve test ratio is: the valve design pressure is less than or equal to 1.0MPa from each batch of random inspection 10% and not less than one Valve test, if unqualified double sampling, if still unqualified, one by one to the valve test; design pressure greater than 1.0MPa valves one by one valve test.
2.2 Commonly used API standards for petrochemical metal water supply and drainage pipelines - Valves, Globe Valves, Butterfly Valves
For petrochemical metal water supply and drainage pipelines commonly used API standard manufacturing valves - gate valve, globe valve, butterfly valve, the proportion of its valve test follows the "Code for acceptance of construction quality of petrochemical metal pipeline engineering" GB50517-2010, namely the design pressure is less than for the SHC5 level Equal to or equal to 1MPa gate valve, globe valve, butterfly valve, the ratio of its valve test is 10% in each batch and not less than one, if there is failure and then random inspection of 20% and not less than one valve test, if unqualified Valve tests were performed one by one, and valves of other pipelines were tested one by one.
3 Conclusion
In the construction of a large-scale petrochemical project, the valves of water supply and drainage pipelines are made of API standard valves and are commonly used as gate valves, globe valves, and butterfly valves. Valves are tested after valve tests according to the above valve test items and test proportions. In the subsequent pipeline tests and pilot tests of the water supply and drainage pipelines, the valves are all normal, and the subsequent production runs provide safe and stable operation of the drainage pipelines, eliminating the previous tests of the water supply and drainage pipelines, commissioning, and normal operation. , Leakage phenomenon, practice has proved that the strict implementation of this valve test project and the proportion of test to ensure the construction quality of petrochemical water supply and drainage pipeline is necessary and reasonable.
Aluminum dropper is a tool used in Cosmetic packaging settings to transfer small amounts of liquid. Aluminum dropper consists of an aluminum shell with a rubber bulb at one end and glass pipette at the other. The dropper is used by squeezing the bulb to draw liquid into the tube and then releasing the bulb to dispense the liquid drop by drop. Material: aluminum, plastic, silicone, glass, etc. Neck size: 13MM, 18MM, 20MM, 22MM, 24MM,Uses: essential oil skin care cosmetic packaging.Support customization.
Aluminum Dropper,Aluminum Medicine Droppers,Glass Dropper,Glass Pipette Dropper
Jiangyin keyi packing Material Co.,Ltd , https://www.keyipacking.com